Psoriasis vs. Eczema: Understanding the Differences
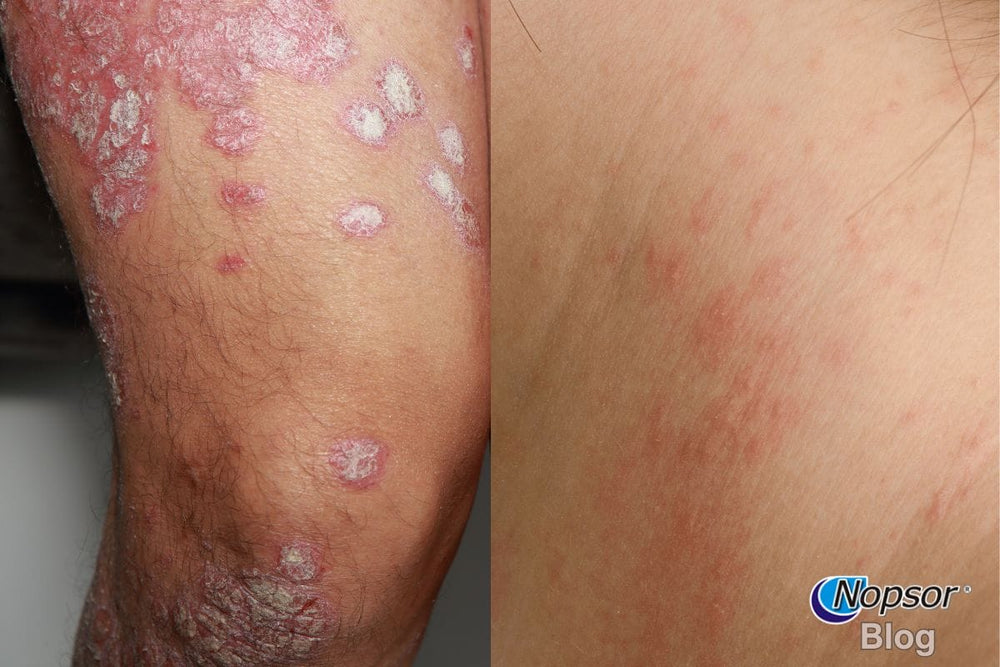
Psoriasis and eczema are two common chronic skin conditions that can cause itching, redness, and inflammation. While they share some similarities, they have distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Understanding the differences between psoriasis vs. eczema can help you identify your condition and find the right treatment.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes the skin to regenerate too quickly, leading to thick, scaly patches on the skin. This condition is caused by an overactive immune response that triggers rapid skin cell production, leading to the buildup of plaque-like lesions.
Key Characteristics of Psoriasis:
✔ Red, inflamed patches covered with silvery-white scales
✔ Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
✔ Itching, burning, or soreness in affected areas
✔ Commonly appears on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back
✔ Often accompanied by psoriatic arthritis (joint pain and stiffness)
Types of Psoriasis:
- Plaque Psoriasis (Most Common): Thick, raised red patches covered with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, drop-like spots that often appear after an infection.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, shiny red lesions that occur in skin folds.
- Pustular Psoriasis: White pustules (blisters) surrounded by inflamed skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare, severe form causing widespread redness and shedding.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects the skin barrier, making it more sensitive and prone to irritation. Unlike psoriasis, eczema is not an autoimmune disease, but it can be triggered by allergens, irritants, and environmental factors.
Key Characteristics of Eczema:
✔ Intense itching that can lead to scratching and skin damage
✔ Red, inflamed, and swollen skin
✔ Oozing blisters that may crust over
✔ Thickened, leathery skin due to long-term scratching
✔ Commonly affects the face, neck, hands, and inside of elbows and knees
Types of Eczema:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Most Common): Chronic, itchy rash often linked to allergies or asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by irritants or allergens, such as soaps or chemicals.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet.
- Nummular Eczema: Circular, coin-shaped patches of irritated skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Red, scaly patches in oily areas like the scalp and face.
Key Differences Between Psoriasis and Eczema
| Feature | Psoriasis | Eczema |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Autoimmune disease | Inflammatory reaction |
| Appearance | Thick, raised red plaques with silvery scales | Red, inflamed, swollen skin with oozing or crusting |
| Itching Level | Mild to moderate (can be painful) | Severe and persistent itching |
| Common Locations | Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back | Face, neck, hands, inside of elbows & knees |
| Triggers | Stress, infections, cold weather, medications | Allergens, irritants, stress, weather changes |
| Treatment Options | Topical steroids, phototherapy, systemic drugs, biologics | Moisturizers, antihistamines, topical steroids |
While both conditions cause inflammation and itching, eczema is more likely to involve fluid-filled blisters and extreme itchiness, while psoriasis is characterized by thicker plaques with scaling.
Diagnosis: How Can You Tell If You Have Psoriasis or Eczema?
If you suspect you have either psoriasis or eczema, a dermatologist can help with a proper diagnosis by:
✔ Conducting a skin examination
✔ Asking about symptoms, triggers, and medical history
✔ Performing a skin biopsy (if necessary) to differentiate between conditions
Because eczema and psoriasis can look similar, it’s crucial to get a professional diagnosis to ensure the right treatment.
Treatment Options: Managing Psoriasis vs. Eczema
Psoriasis Treatment
Since psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, treatments focus on reducing inflammation and slowing skin cell growth:
✔ Topical Treatments: Steroid creams, vitamin D analogs, coal tar, and salicylic acid.
✔ Phototherapy: UV light therapy to slow skin cell production.
✔ Systemic Medications: Immunosuppressants (methotrexate, cyclosporine) or biologics (adalimumab, secukinumab).
✔ Natural Treatments: Moisturizers, anti-inflammatory diets, and stress reduction.
✔ Nopsor Treatment: A steroid-free, natural treatment containing coal tar and salicylic acid, designed for nightly application to reduce scaling and inflammation. Learn more at www.nopsor-usa.com.
Eczema Treatment
Since eczema is caused by an overreactive immune response to irritants, treatment focuses on moisturizing and reducing inflammation:
✔ Moisturizers: Thick emollients to lock in moisture.
✔ Topical Steroids: Reduce inflammation and redness.
✔ Antihistamines: Help relieve itching.
✔ Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens (soaps, perfumes, pet dander).
✔ Wet Wrap Therapy: Wrapping affected areas with damp bandages to retain moisture.
Can You Have Both Psoriasis and Eczema?
Yes! It is possible to have both psoriasis and eczema at the same time, though this is rare. In some cases, a person may have psoriasis on some areas of the body and eczema on others. If your symptoms overlap, a dermatologist can help determine the best treatment approach.
Which Condition Is More Serious?
Both conditions can significantly impact quality of life, but psoriasis is generally more associated with systemic inflammation, meaning it can lead to:
✔ Increased risk of psoriatic arthritis (joint pain and stiffness).
✔ Higher likelihood of cardiovascular disease and diabetes due to chronic inflammation.
✔ Possible links to mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
Eczema, on the other hand, is more commonly associated with allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever but doesn’t usually carry the same long-term systemic risks as psoriasis.
Final Thoughts: Which One Do You Have?
If you’re experiencing chronic skin irritation, redness, or itching, it's important to see a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. Understanding whether you have psoriasis vs. eczema will help you get the right treatment and manage your symptoms effectively.
✔ Psoriasis: More scaly, thickened plaques that are less itchy.
✔ Eczema: More inflamed, itchy, and weepy skin.
No matter which condition you have, proper skin care and treatment can make a huge difference in reducing flare-ups and improving quality of life.
For natural psoriasis relief, explore Nopsor’s specialized psoriasis treatment, designed to help soothe and support irritated skin. Learn more at www.nopsor-usa.com.
References
-
National Eczema Association - Eczema or Psoriasis?
This article discusses the differences in appearance, affected areas, and symptoms between eczema and psoriasis.
https://nationaleczema.org/blog/eczema-or-psoriasis/ -
Medical News Today - Psoriasis vs. Eczema: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
This article explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for both conditions, helping readers understand their differences.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/315749 -
Healthline - Eczema vs. Psoriasis: Differences, Symptoms, and Treatment
This comprehensive guide outlines the distinctions between eczema and psoriasis, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment strategies.
https://www.healthline.com/health/psoriasis/eczema-vs-psoriasis


Leave a comment
Also in Psoriasis 101
What is Psoriasis? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
December 16, 2024
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes red, scaly patches on the skin. Learn about its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Continue reading
Psoriasis Treatment Guide: 10 Questions to Ask Your Dermatologist
December 10, 2024
Continue reading
Frequently Asked Questions About Psoriasis Treatment Options
December 09, 2024
Continue reading